Full metadata record
| DC Field | Value | Language |
|---|---|---|
| dc.creator | Zalba, S. (Sara) | - |
| dc.creator | Navarro-Blasco, I. (Iñigo) | - |
| dc.creator | Troconiz, I.F. (Iñaki F.) | - |
| dc.creator | Tros-de-Ilarduya, C. (Conchita) | - |
| dc.creator | Garrido, M.J. (María Jesús) | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2012-03-07T17:33:28Z | - |
| dc.date.available | 2012-03-07T17:33:28Z | - |
| dc.date.issued | 2012 | - |
| dc.identifier.citation | Zalba S, Navarro I, Troconiz IF, Ilarduya CT, Garrido MJ. Application of different methods to formulate PEG-liposomes of oxaliplatin: Evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012 Feb 18. | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0939-6411 | - |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/10171/21016 | - |
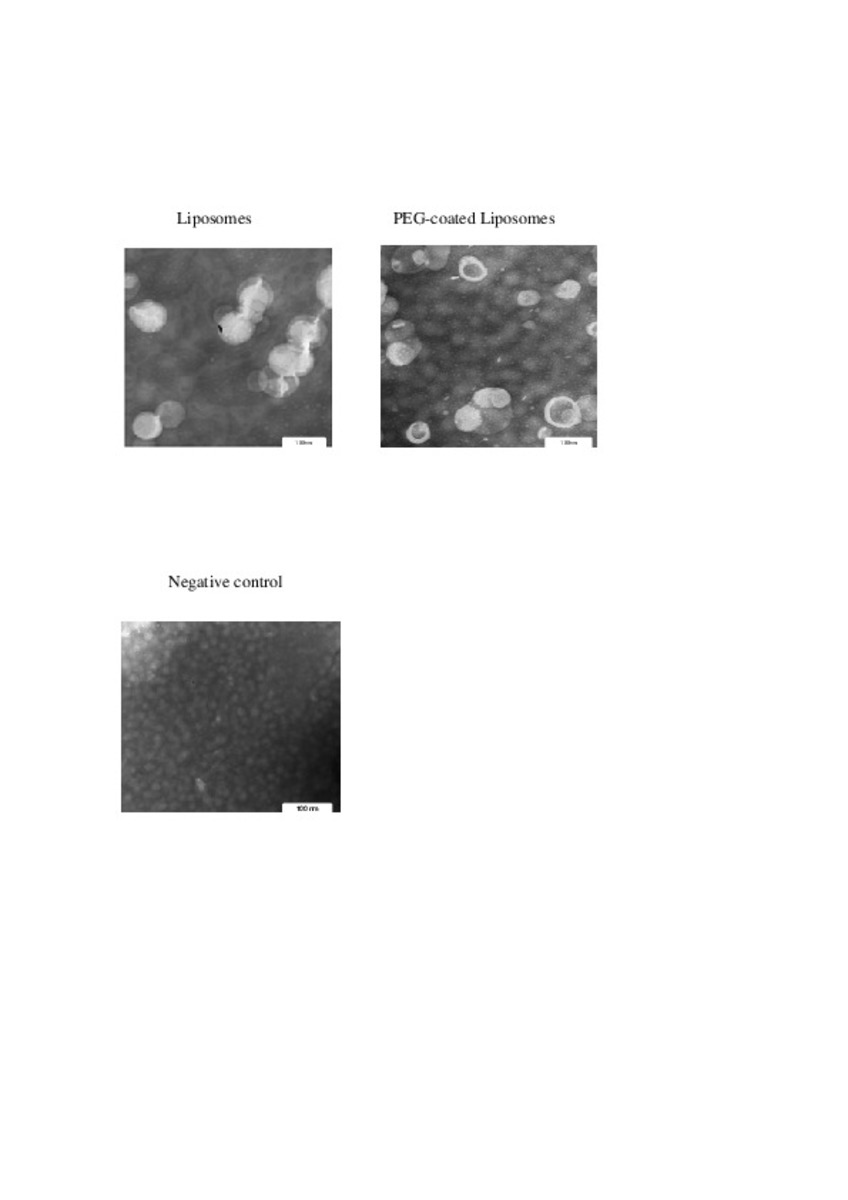
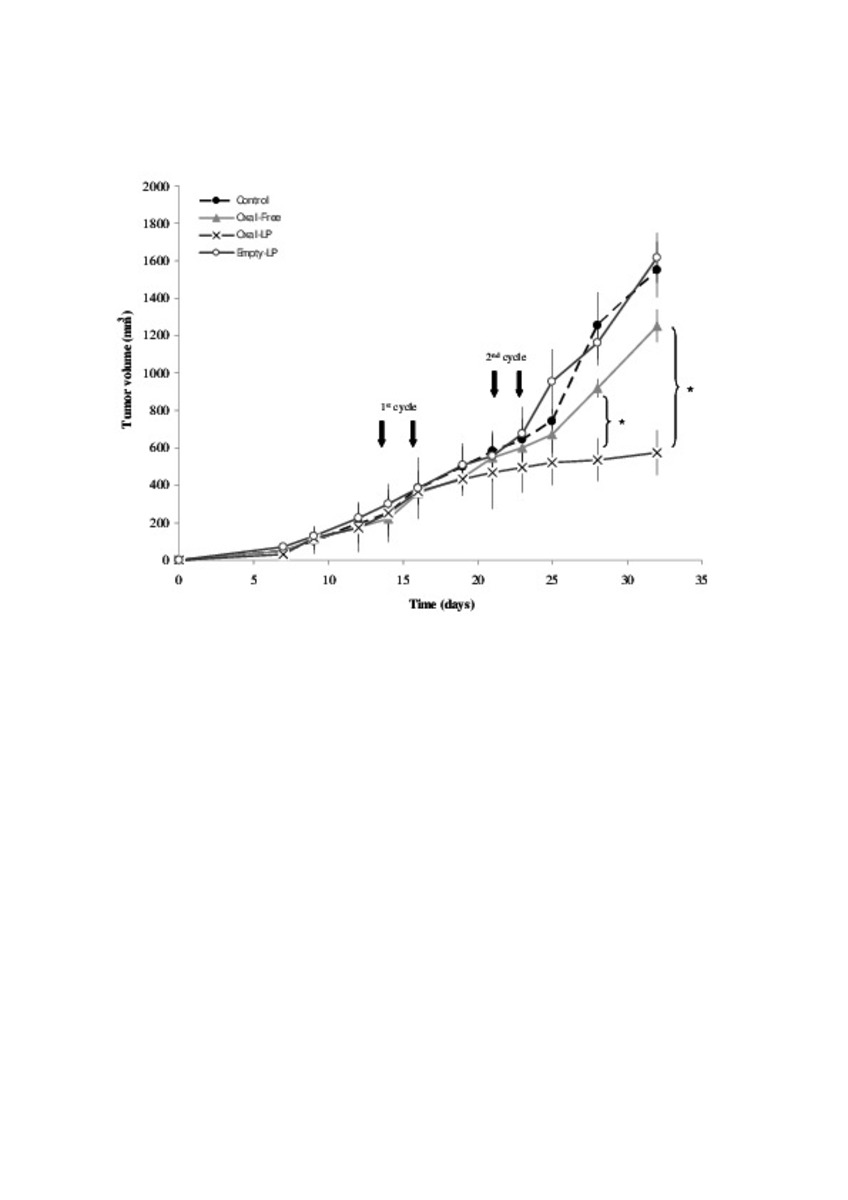
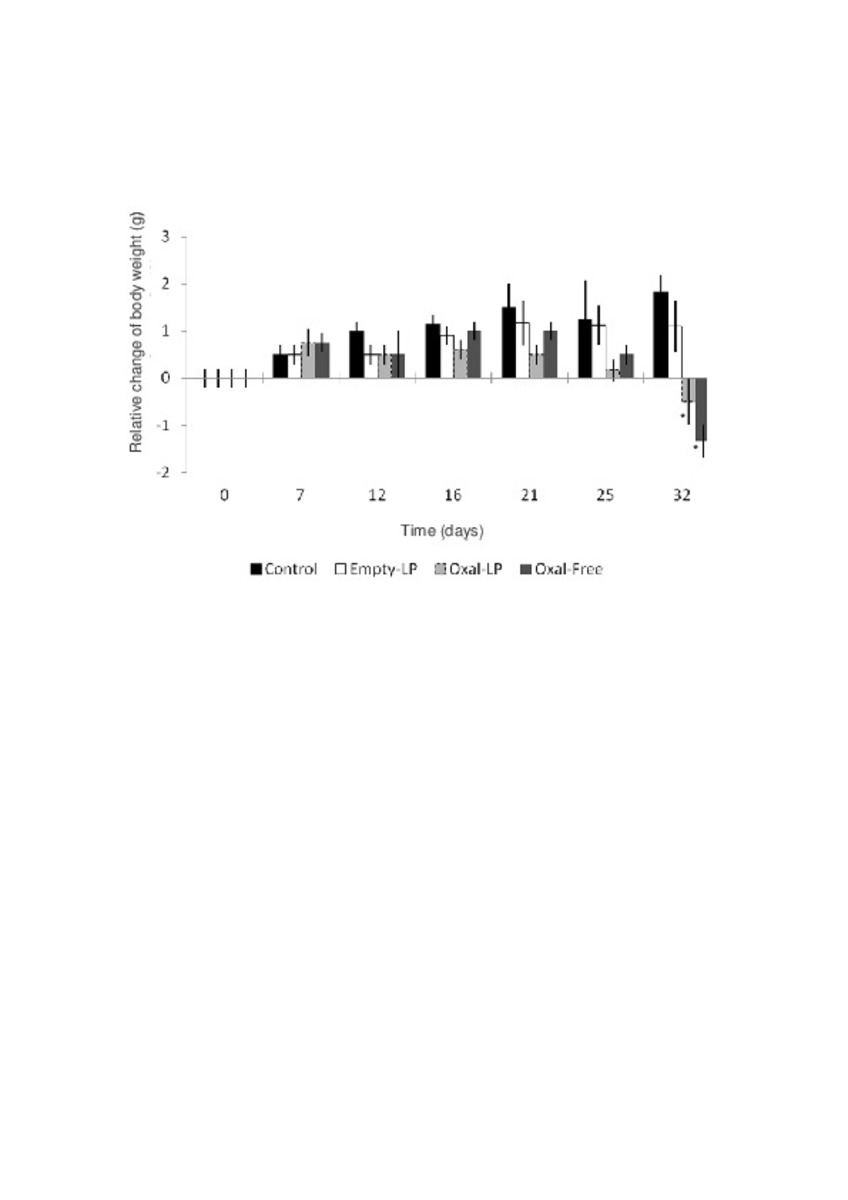
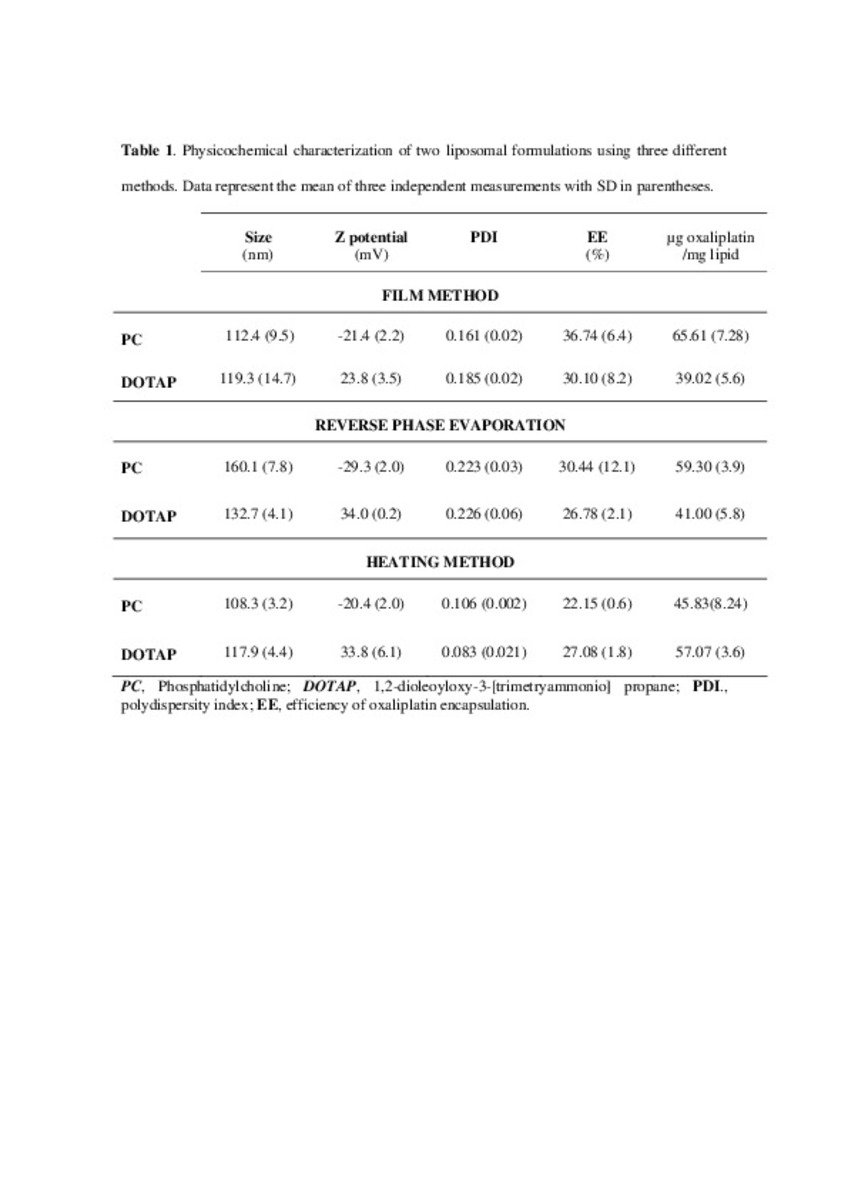
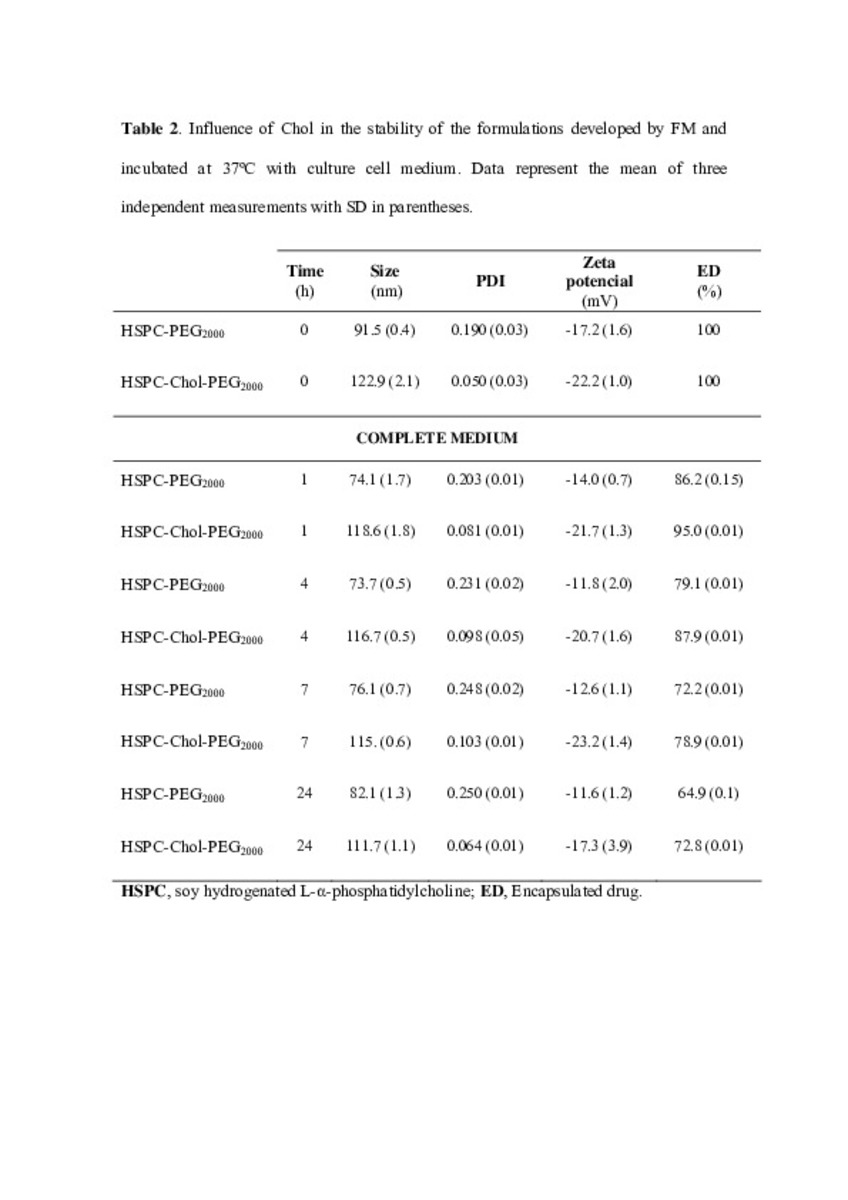
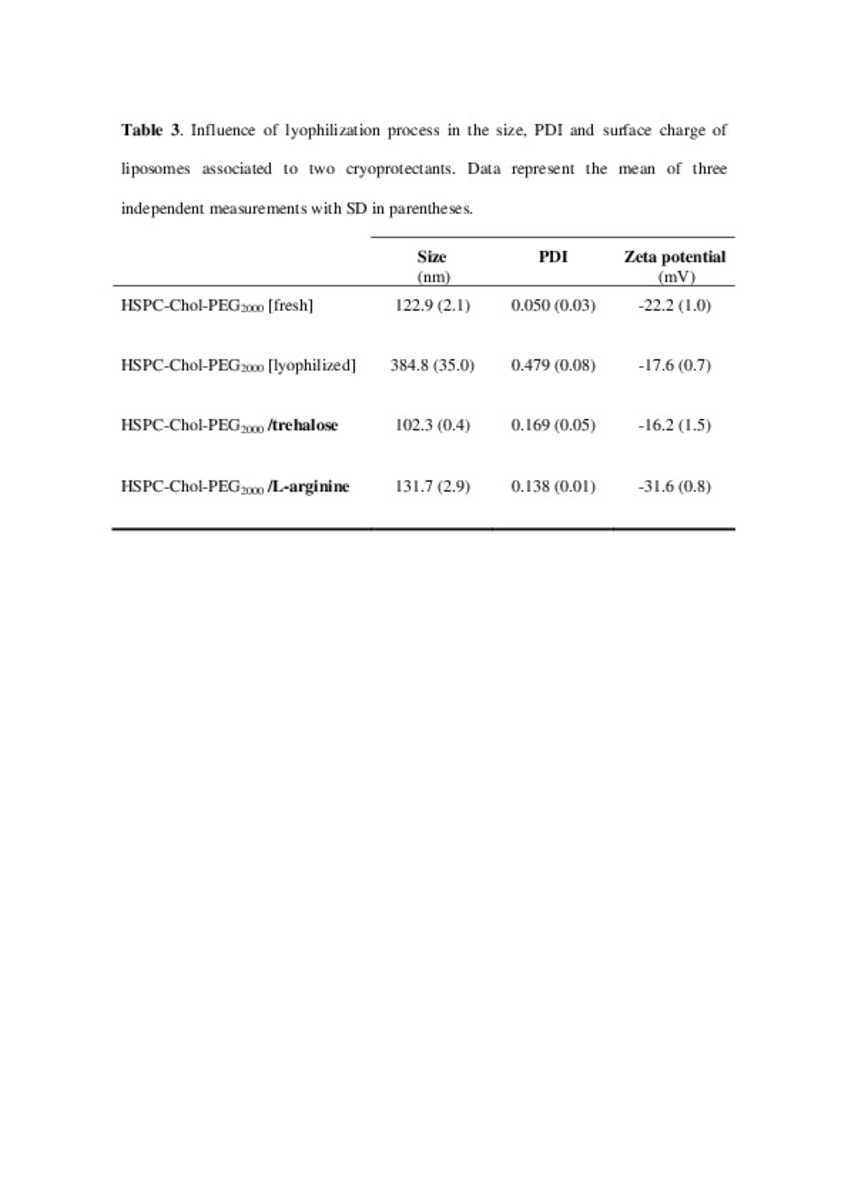
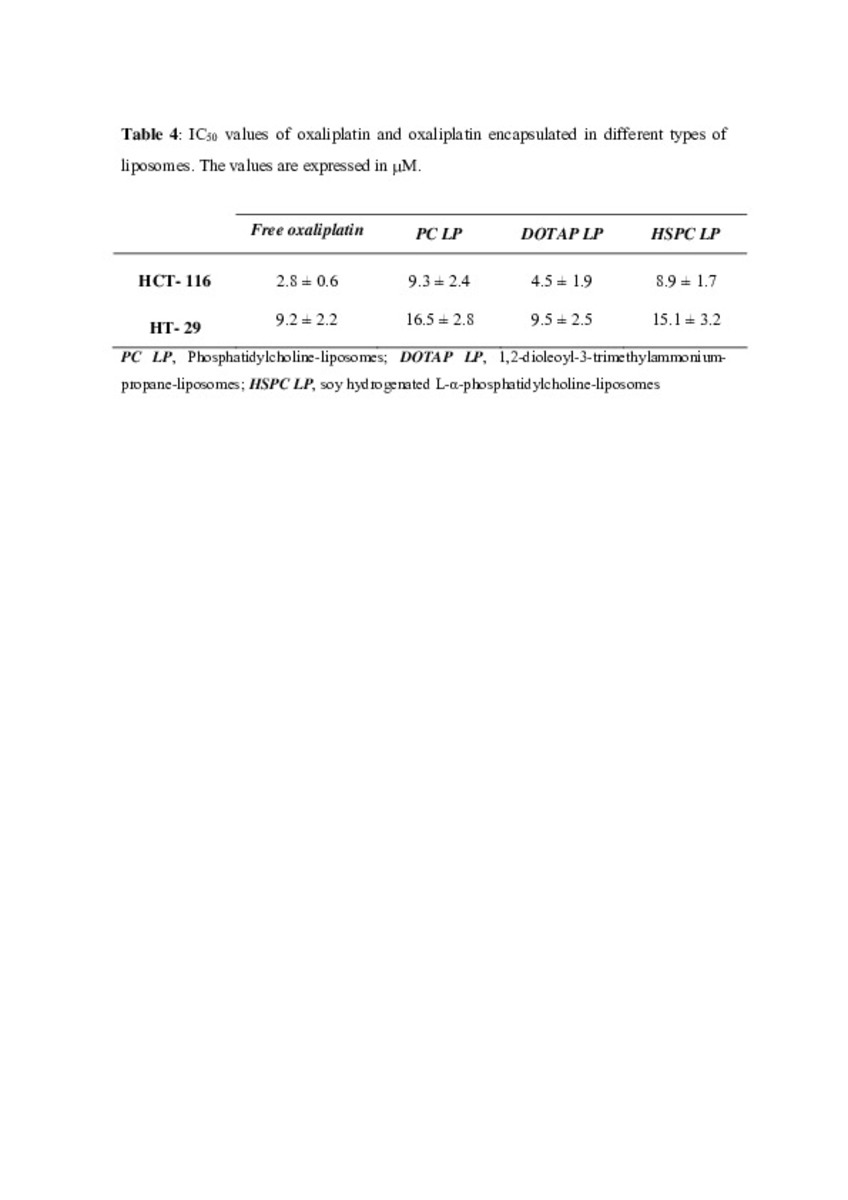
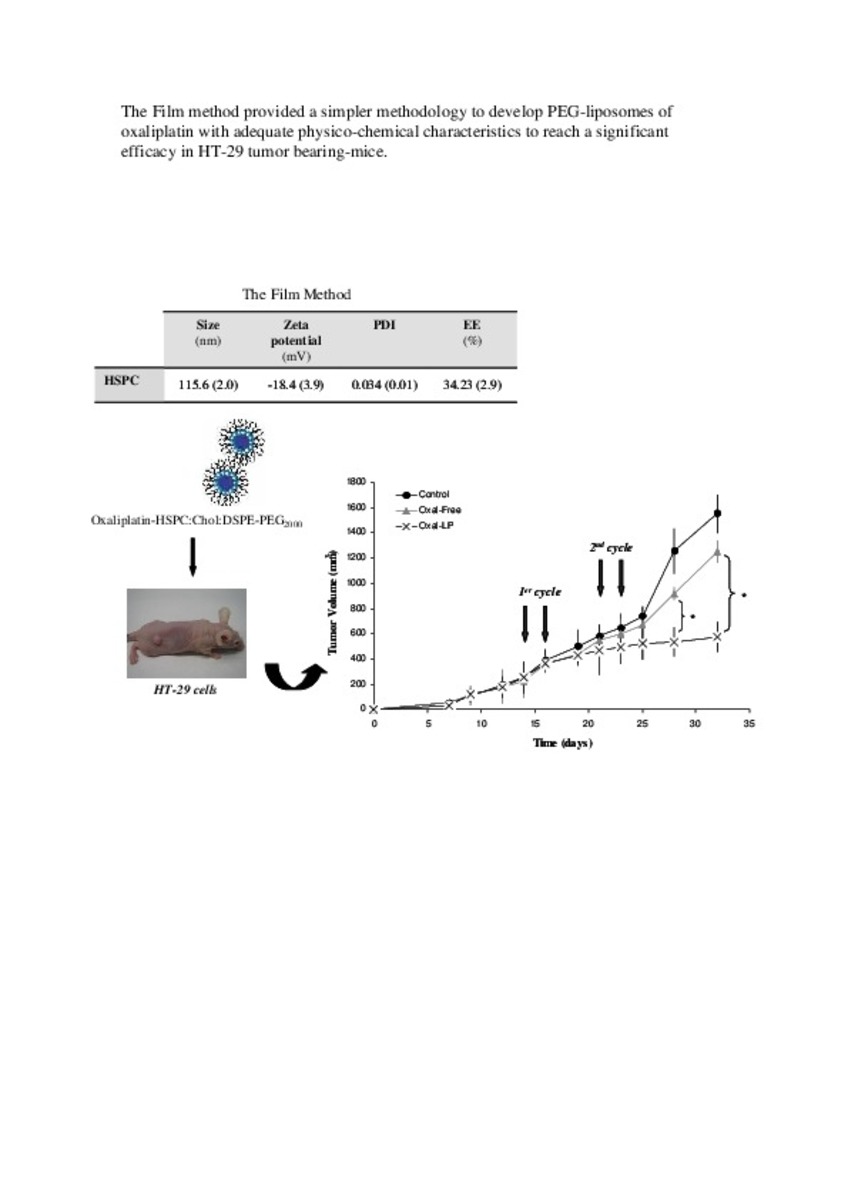
| dc.description.abstract | In this work the film method (FM), reverse-phase evaporation (REV) and the heating method (HM) were applied to prepare PEG-coated liposomes of oxaliplatin with natural neutral and cationic lipids, respectively. The formulations developed with the three methods, showed similar physicochemical characteristics, except in the loading of oxaliplatin, which was statistically lower (P<0.05) using the HM. The incorporation of a semi-synthetic lipid in the formulation developed by FM, provided liposomes with a particle size of 115 nm associated to the lowest polydispersity index and the highest drug loading, 35%, compared to the other two lipids, suggesting an increase of the membrane stability. That stability was also evaluated according to the presence of cholesterol, the impact of the temperature, and the application of different cryoprotectans during the lyophilization. The results indicated long-term stability of the developed formulation, because after its intravenous in-vivo administration to HT-29 tumor bearing mice was able to induce an inhibition of tumor growth statistically higher (P < 0.05) than the inhibition caused by the free drug. In conclusion, the FM was the simplest method in comparison with REV and HM to develop in vivo stable and efficient PEG-coated liposomes of oxaliplatin with a loading higher than those reported for REV. | es_ES |
| dc.language.iso | eng | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | Elsevier | es_ES |
| dc.rights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Film method | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Reverse-Phase evaporation method | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Heating method | es_ES |
| dc.subject | PEG-coated liposomes | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Oxaliplatin | es_ES |
| dc.title | Application of different methods to formulate PEG-liposomes of oxaliplatin: Evaluation in vitro and in vivo | es_ES |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article | es_ES |
| dc.type.driver | info:eu-repo/semantics/article | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.doi | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.02.007 | es_ES |
Files in This Item:
Statistics and impact
Items in Dadun are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.