Full metadata record
| DC Field | Value | Language |
|---|---|---|
| dc.creator | Imbuluzqueta, E. (Edurne) | - |
| dc.creator | Gamazo, C. (Carlos) | - |
| dc.creator | Lana, H. (Hugo) | - |
| dc.creator | Campanero, M.A. (Miguel Angel) | - |
| dc.creator | Salas, D. (David) | - |
| dc.creator | Gil, A.G. (Ana Gloria) | - |
| dc.creator | Elizondo, E. (Elisa) | - |
| dc.creator | Ventosa, N. (Nora) | - |
| dc.creator | Veciana, J. (Jaume) | - |
| dc.creator | Blanco-Prieto, M.J. (María José) | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-12-23T11:31:54Z | - |
| dc.date.available | 2013-12-23T11:31:54Z | - |
| dc.date.issued | 2013 | - |
| dc.identifier.citation | Imbuluzqueta E, Gamazo C, Lana H, Campanero MA, Salas D, Gil AG, et al. Hydrophobic gentamicin-loaded nanoparticles are effective against Brucella melitensis infection in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013 2013 Jul (Epub 2013 May 06);57(7):3326-3333 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0066-4804 | - |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/10171/34787 | - |
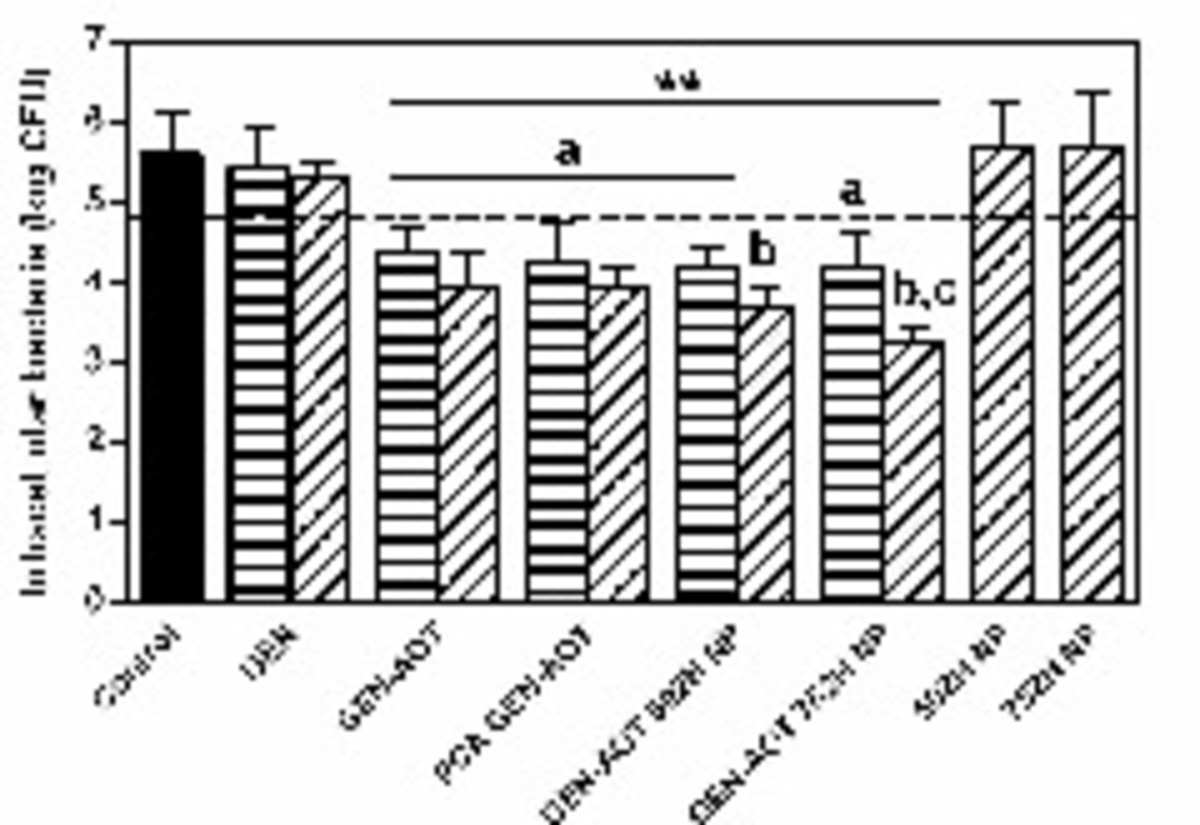
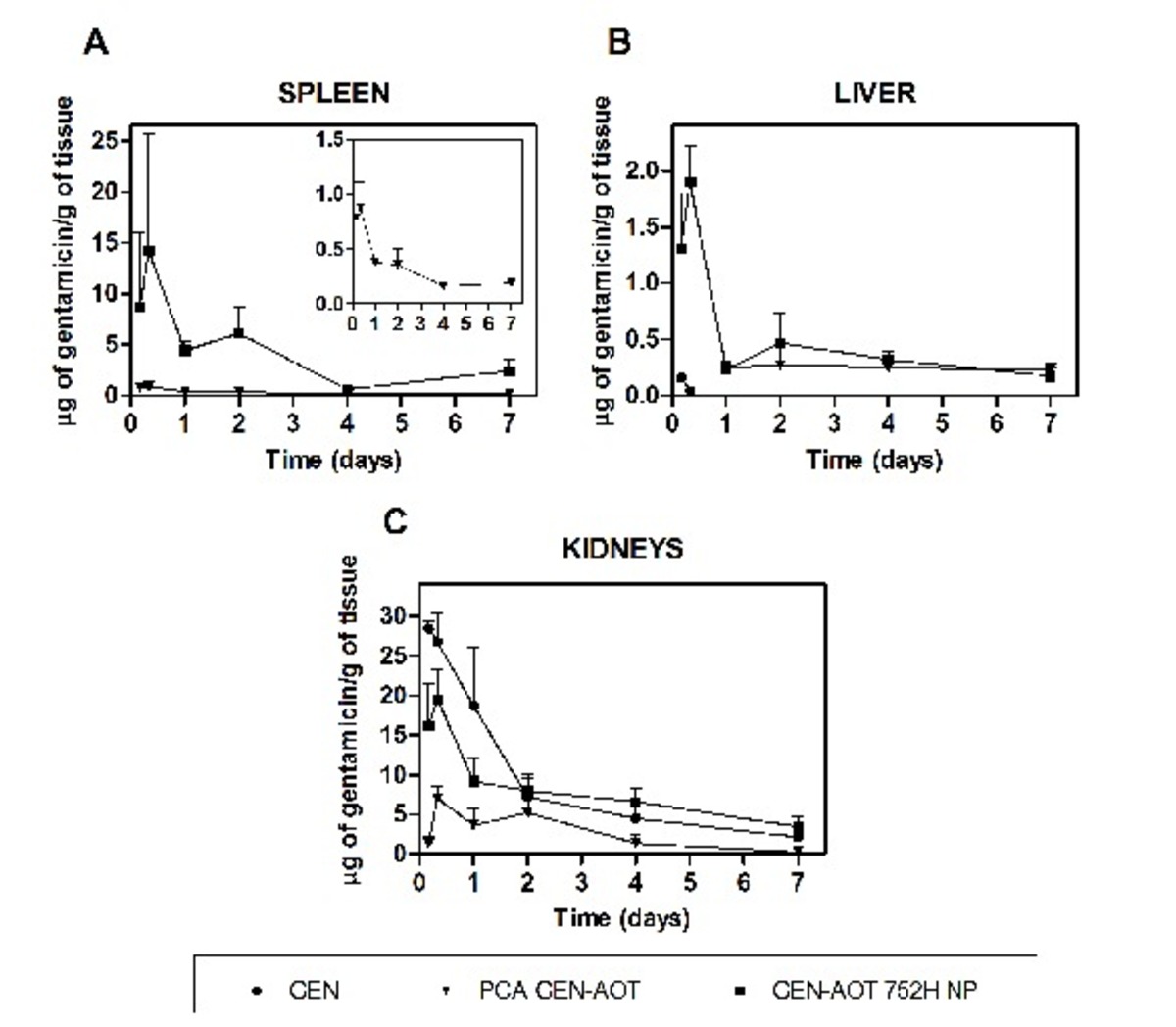
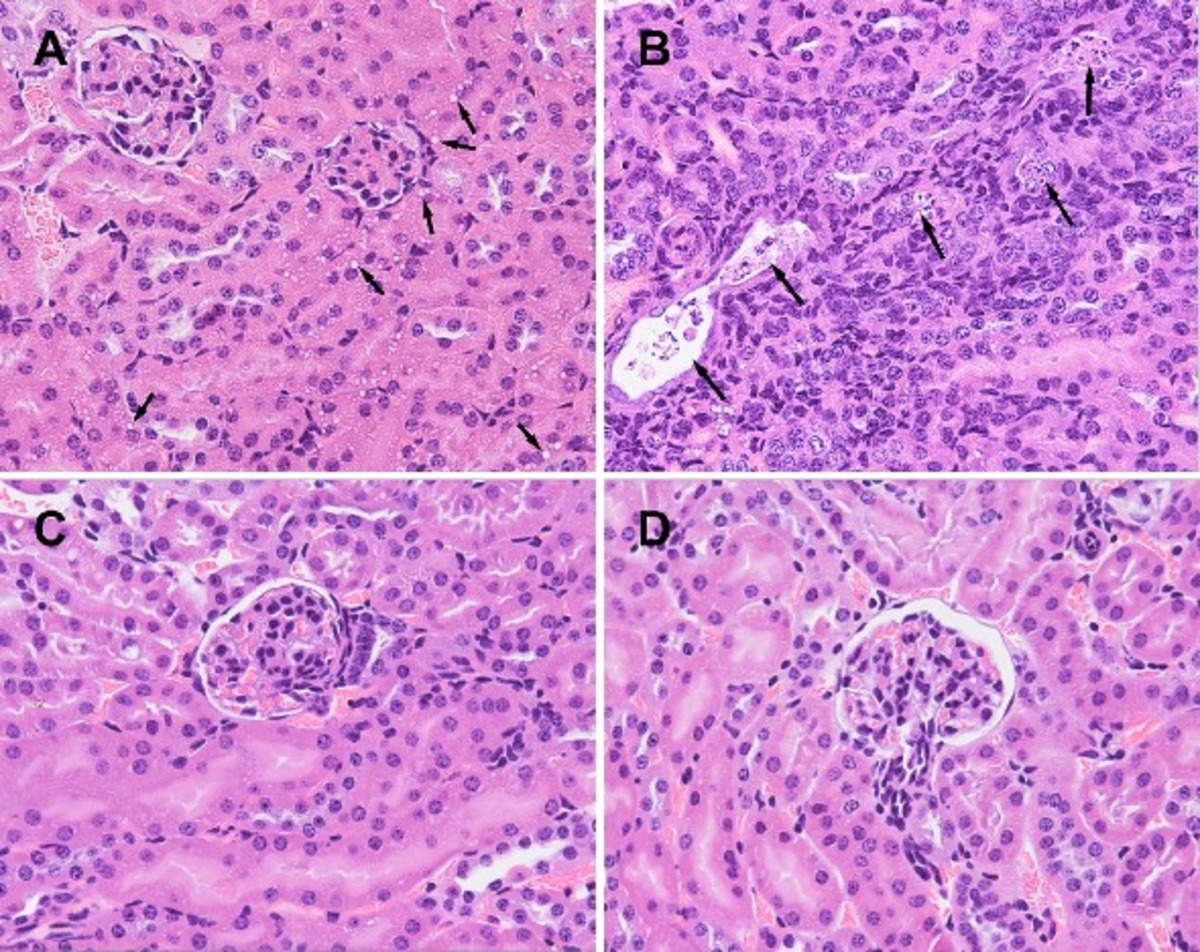
| dc.description.abstract | The clinical management of human brucellosis is still challenging and demands in vitro active antibiotics capable of targeting the pathogen-harboring intracellular compartments. A sustained release of the antibiotic at the site of infection would make it possible to reduce the number of required doses and thus the treatment-associated toxicity. In this study, a hydrophobically modified gentamicin, gentamicin-AOT [AOT is bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate sodium salt], was either microstructured or encapsulated in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles. The efficacy of the formulations developed was studied both in vitro and in vivo. Gentamicin formulations reduced Brucella infection in experimentally infected THP-1 monocytes (>2-log10 unit reduction) when using clinically relevant concentrations (18 mg/liter). Moreover, in vivo studies demonstrated that gentamicin-AOT-loaded nanoparticles efficiently targeted the drug both to the liver and the spleen and maintained an antibiotic therapeutic concentration for up to 4 days in both organs. This resulted in an improved efficacy of the antibiotic in experimentally infected mice. Thus, while 14 doses of free gentamicin did not alter the course of the infection, only 4 doses of gentamicin-AOT-loaded nanoparticles reduced the splenic infection by 3.23 logs and eliminated it from 50% of the infected mice with no evidence of adverse toxic effects. These results strongly suggest that PLGA nanoparticles containing chemically modified hydrophobic gentamicin may be a promising alternative for the treatment of human brucellosis. | es_ES |
| dc.language.iso | eng | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | American Society for Microbiology | es_ES |
| dc.rights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess | es_ES |
| dc.title | Hydrophobic gentamicin-loaded nanoparticles are effective against Brucella melitensis infection in mice | es_ES |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.doi | http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00378-13 | - |
Statistics and impact
Items in Dadun are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.