Full metadata record
| DC Field | Value | Language |
|---|---|---|
| dc.creator | Garbayo, E | - |
| dc.creator | Ansorena-Artieda, E. (Eduardo) | - |
| dc.creator | Blanco-Prieto, M.J. (María José) | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-12-23T11:40:02Z | - |
| dc.date.available | 2013-12-23T11:40:02Z | - |
| dc.date.issued | 2013 | - |
| dc.identifier.citation | Garbayo E, Ansorena E, Blanco-Prieto MJ. Drug development in Parkinson's disease: From emerging molecules to innovative drug delivery systems. Maturitas 2013 2013 Nov;76(3):272-278 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1873-4111 | - |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/10171/34788 | - |
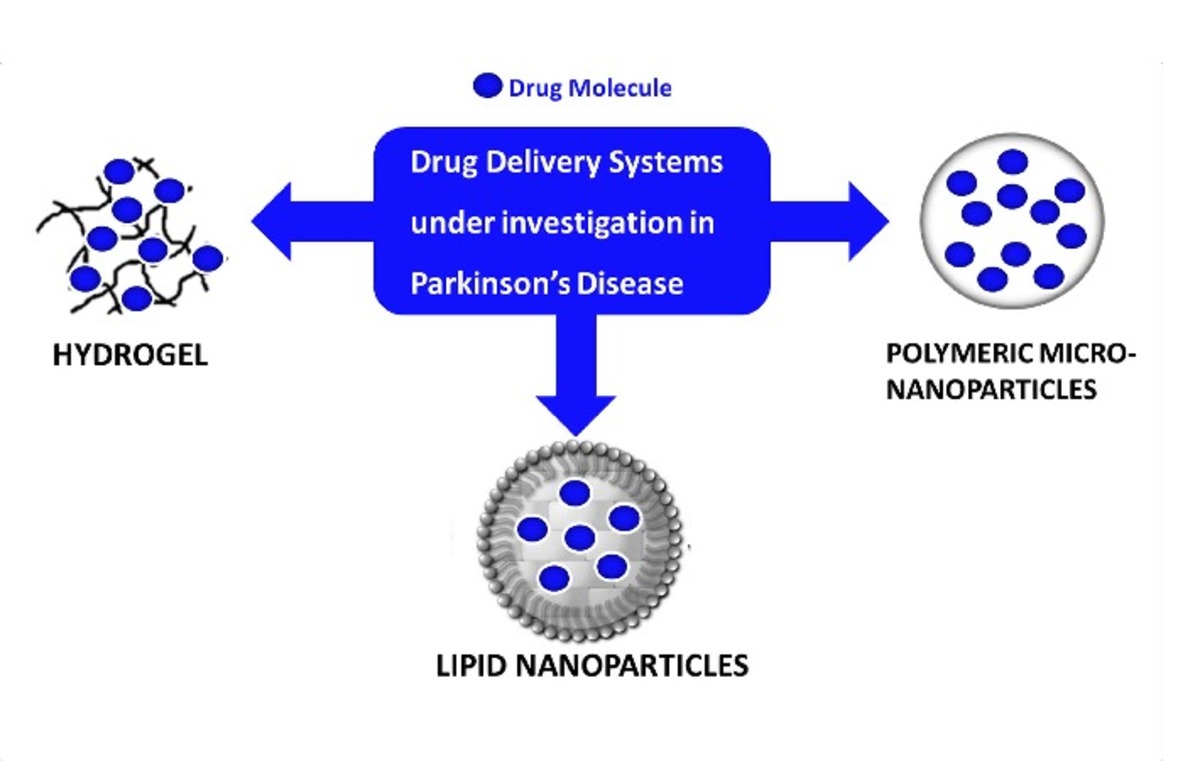
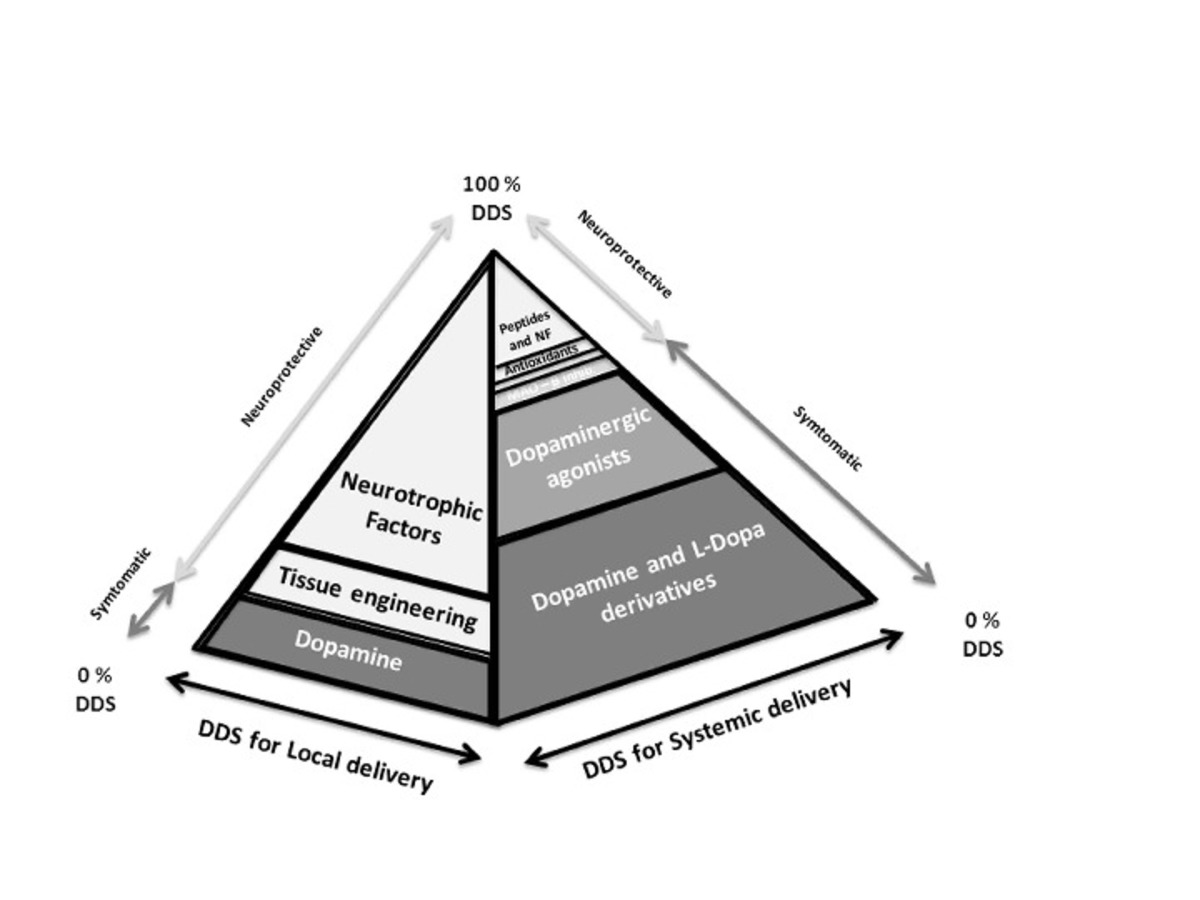
| dc.description.abstract | Current treatments for Parkinson’s disease (PD) are aimed at addressing motor symptoms but there is no therapy focused on modifying the course of the disease. Successful treatment strategies have been so far limited and brain drug delivery remains a major challenge that restricts its treatment. This review provides an overview of the most promising emerging agents in the field of PD drug discovery, discussing improvements that have been made in brain drug delivery for PD. It will be shown that new approaches able to extend the length of the treatment, to release the drug in a continuous manner or to cross the blood brain barrier and target a specific region are still needed. Overall, the results reviewed here show that there is an urgent need to develop both symptomatic and disease-modifying treatments, giving priority to neuroprotective treatments. Promising perspectives are being provided in this field by rasagiline and by neurotrophic factors like glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. The identification of disease-relevant genes has also encouraged the search for disease-modifying therapies that function by identifying molecularly-targeted drugs. The advent of new molecular and cellular targets like α-synuclein, leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine protein kinase 2 or parkin, among others, will require innovative delivery therapies. In this regard, drug delivery systems (DDS) have shown great potential for improving the efficacy of conventional and new PD therapy and reducing its side effects. The new DDS discussed here, which include microparticles, nanoparticles and hydrogels among others, will probably open up possibilities that extend beyond symptomatic relief. However, further work needs to be done before DDS become a therapeutic option for PD patients. | es_ES |
| dc.language.iso | eng | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | Elsevier | es_ES |
| dc.rights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Drug delivery systems | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Parkinson’s disease | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Symptomatic and Disease modifying treatments | es_ES |
| dc.title | Drug development in Parkinson's disease: From emerging molecules to innovative drug delivery systems | es_ES |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.doi | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.05.019 | - |
Statistics and impact
Items in Dadun are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.