Full metadata record
| DC Field | Value | Language |
|---|---|---|
| dc.creator | Díaz-Herráez, P. (Paula) | - |
| dc.creator | Garbayo, E | - |
| dc.creator | Simon-Yarza, T. (Teresa) | - |
| dc.creator | Formiga, F.R. (Fabio R.) | - |
| dc.creator | Prosper-Cardoso, F. (Felipe) | - |
| dc.creator | Blanco-Prieto, M.J. (María José) | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-12-23T15:15:14Z | - |
| dc.date.available | 2013-12-23T15:15:14Z | - |
| dc.date.issued | 2013 | - |
| dc.identifier.citation | Diaz-Herraez P, Garbayo E, Simon-Yarza T, Formiga FR, Prosper F, Blanco-Prieto MJ. Adipose-derived stem cells combined with Neuregulin-1 delivery systems for heart tissue engineering. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2013 SEP;85(1):143-150 | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.issn | 0939-6411 | - |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/10171/34789 | - |
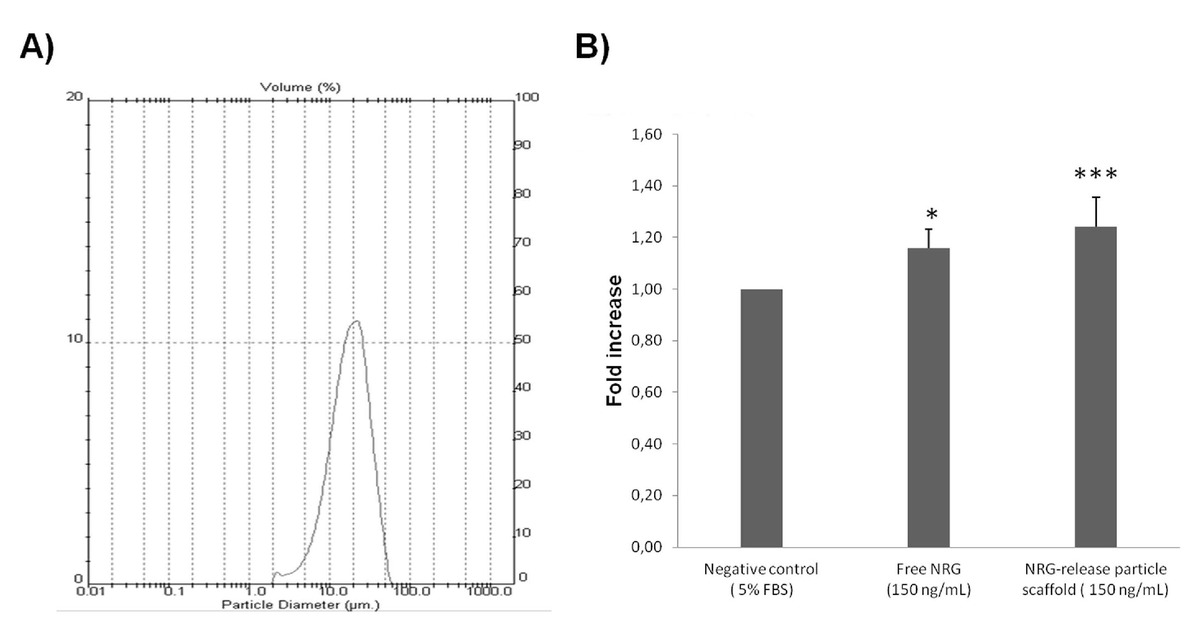
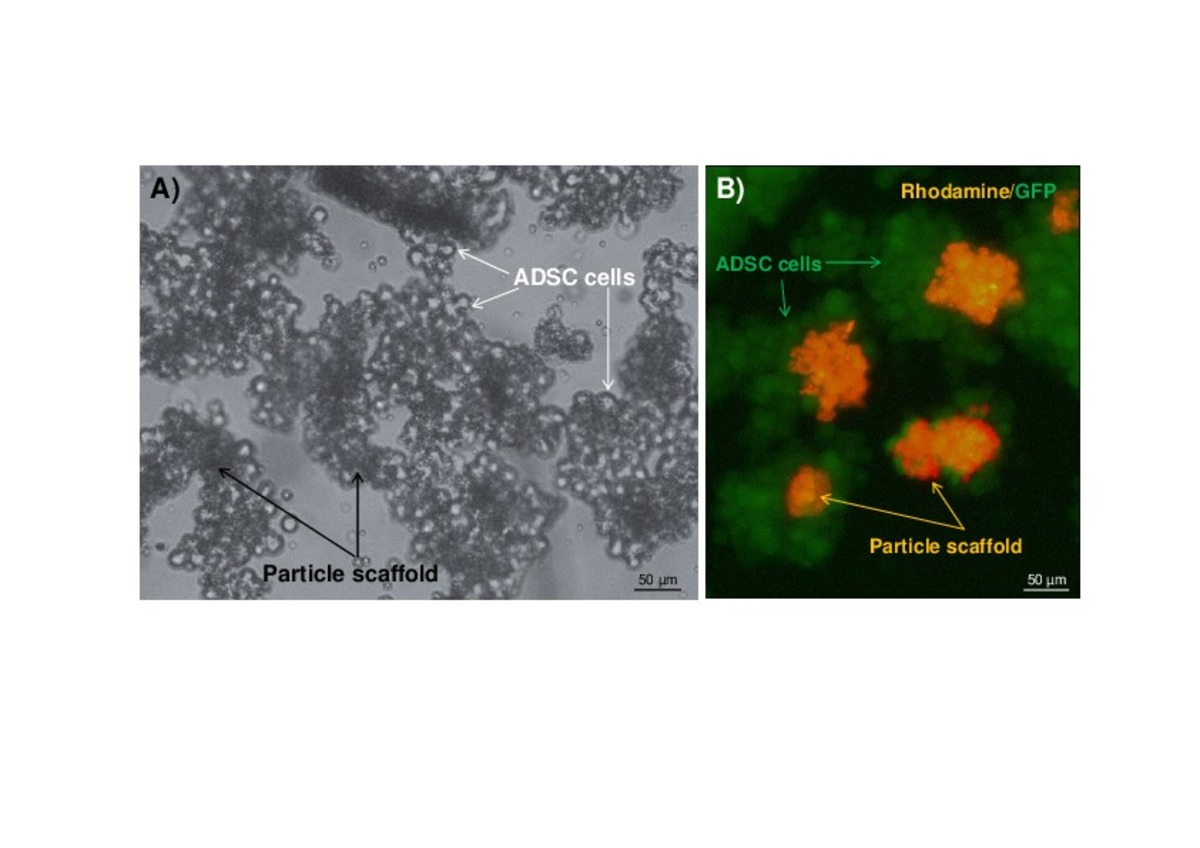
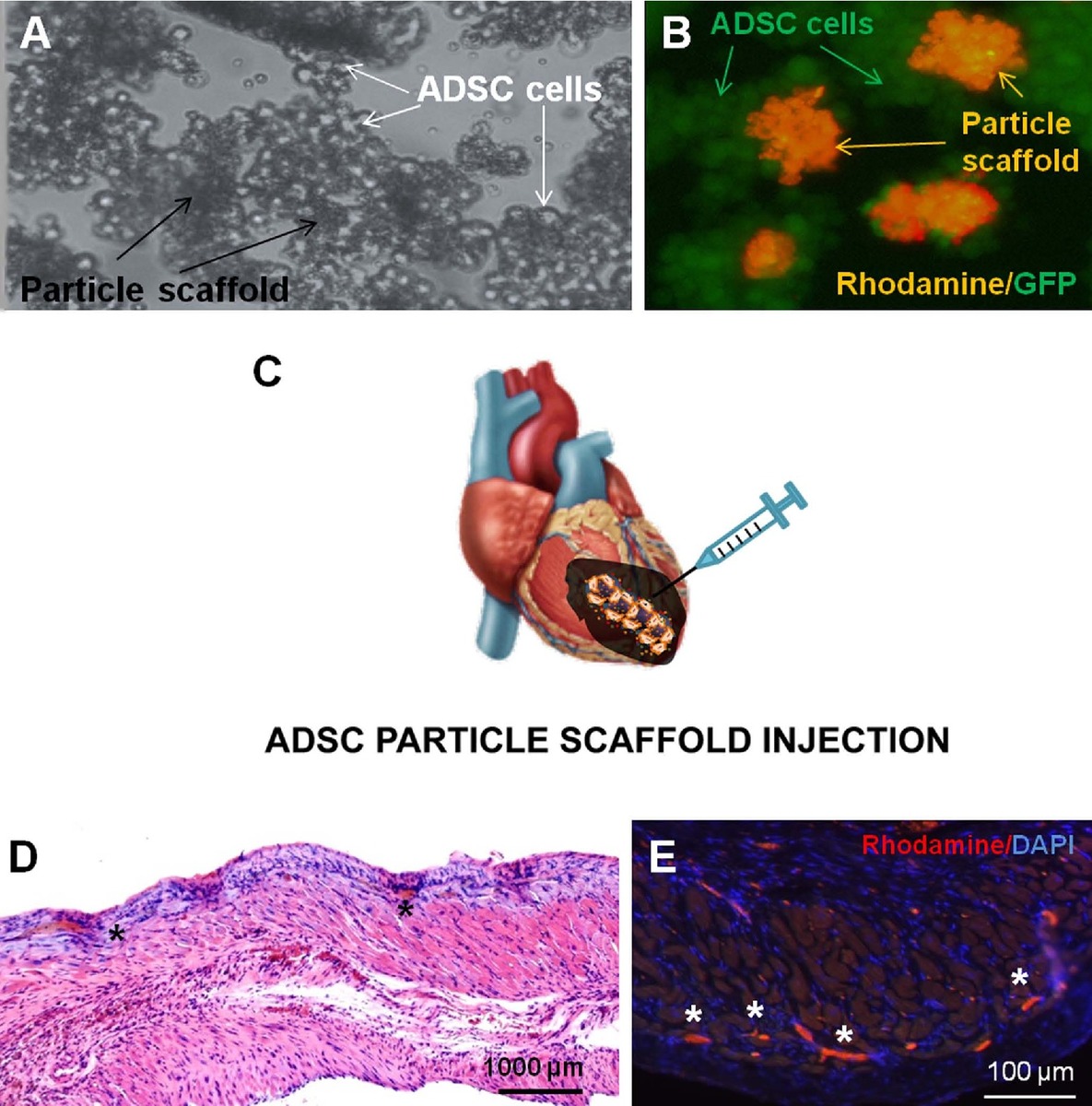
| dc.description.abstract | Myocardial infarction (MI) is the leading cause of death worldwide and extensive research has therefore been performed to find a cure. Neuregulin-1 (NRG) is a growth factor involved in cardiac repair after MI. We previously described how biocompatible and biodegradable microparticles, which are able to release NRG in a sustained manner, represent a valuable approach to avoid problems related to the short half-life after systemic administration of proteins. The effectiveness of this strategy could be improved by combining NRG with several cytokines involved in cardiac regeneration. The present study investigates the potential feasibility of using NRG-releasing particle scaffold combined with adipose derived stem cells (ADSC) as a multiple growth factor delivery-based tissue engineering strategy for implantation in the infarcted myocardium. NRG-releasing particle scaffolds with a suitable size for intramyocardial implantation were prepared by TROMS. Next, ADSC were adhered to particle scaffolds and their potential for heart administration was assessed in a MI rat model. NRG was successfully encapsulated reaching encapsulation efficiencies of 92.58 ± 3.84 %. NRG maintained its biological activity after the microencapsulation process. ADSC cells adhered efficiently to particle scaffolds within a few hours. The ADSC-cytokine delivery system developed proved to be compatible with intramyocardial administration in terms of injectability through a 23-gauge needle and tissue response. Interestingly, ADSC-scaffolds were present in the peri-infarted tissue two weeks after implantation. This proof of concept study provides important evidence required for future effectiveness studies and for the translation of this approach. | es_ES |
| dc.language.iso | eng | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | Elsevier | es_ES |
| dc.rights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Particle scaffold | es_ES |
| dc.subject | PLGA Microparticles | es_ES |
| dc.subject | ADSC | es_ES |
| dc.subject | NRG-1 | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Myocardial infarction | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Cardiac repair | es_ES |
| dc.title | Adipose-derived stem cells combined with Neuregulin-1 delivery systems for heart tissue engineering | es_ES |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.doi | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.03.022 | - |
Statistics and impact
Items in Dadun are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.