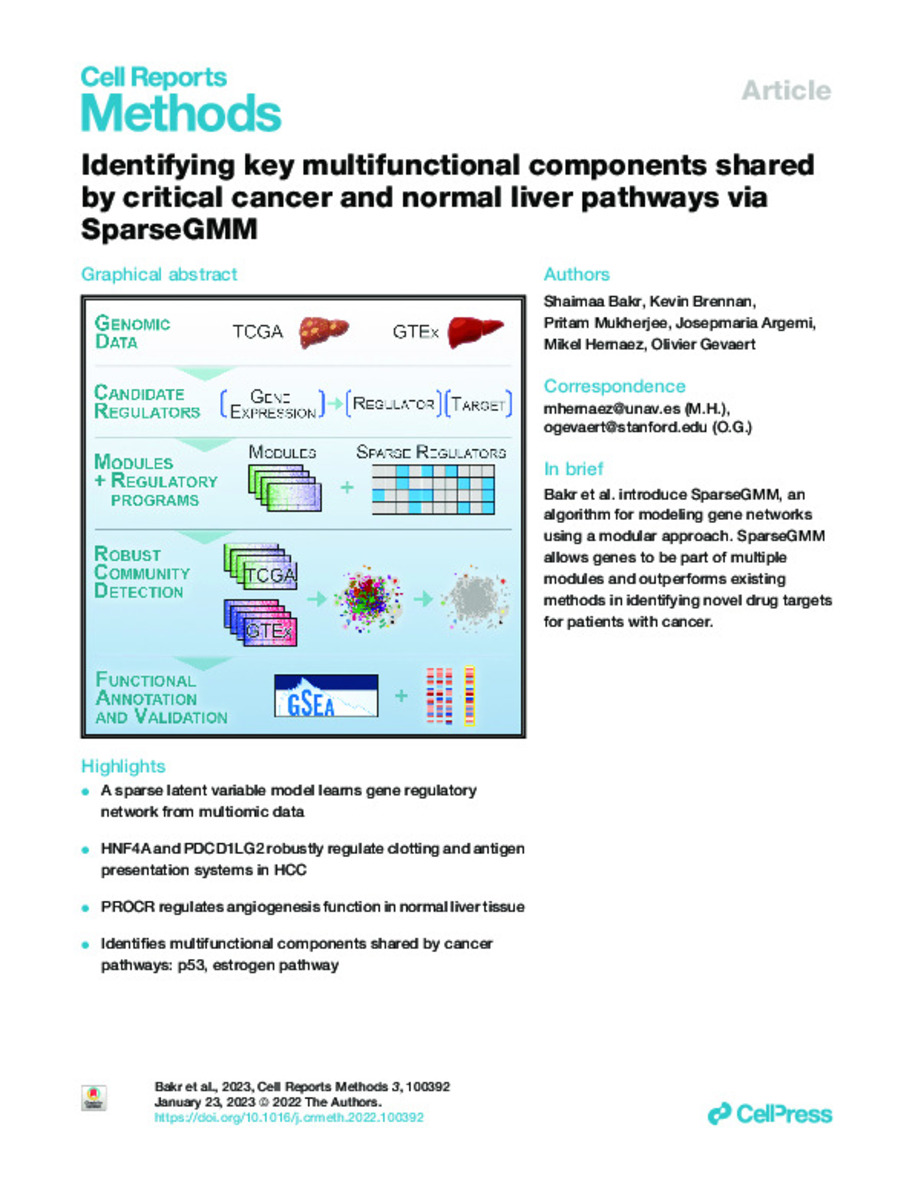
Identifying key multifunctional components shared by critical cancer and normal liver pathways via SparseGMM
Fecha de publicación :
2023
Nota:
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license
Cita:
Bakr, S.; Brennan, K.; Mukherjee, P.; et al. "Identifying key multifunctional components shared by critical cancer and normal liver pathways via SparseGMM". Cell Reports Methods. 3 (1), 2023, 100392
Aparece en las colecciones:
Estadísticas e impacto
0 citas en

0 citas en

Los ítems de Dadun están protegidos por copyright, con todos los derechos reservados, a menos que se indique lo contrario.