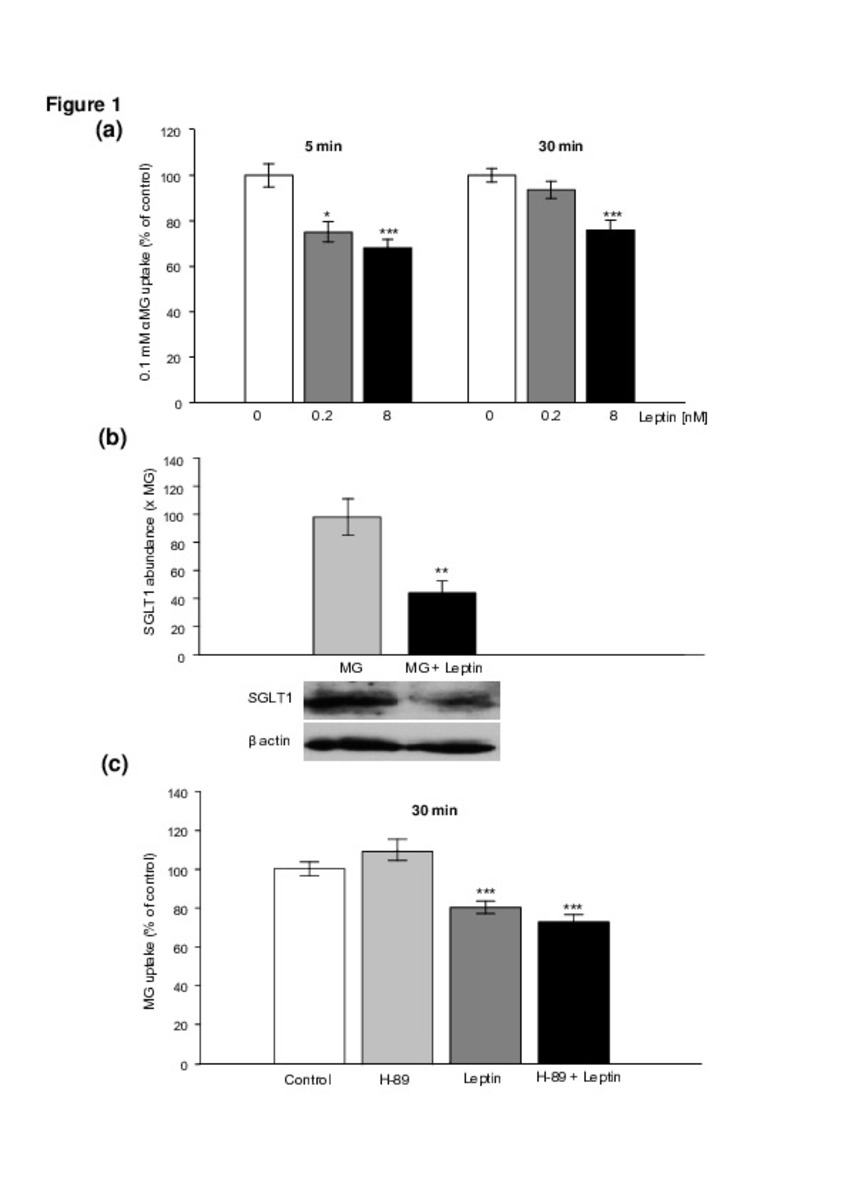
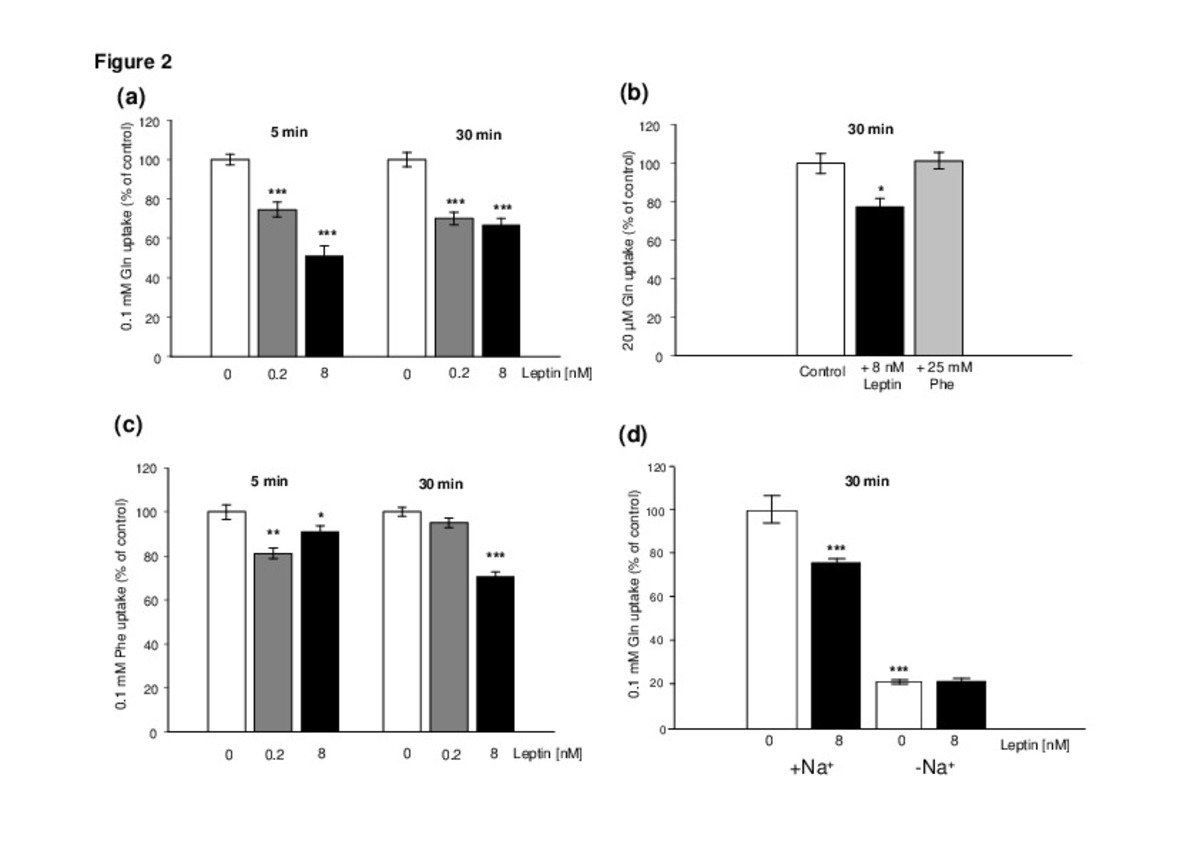
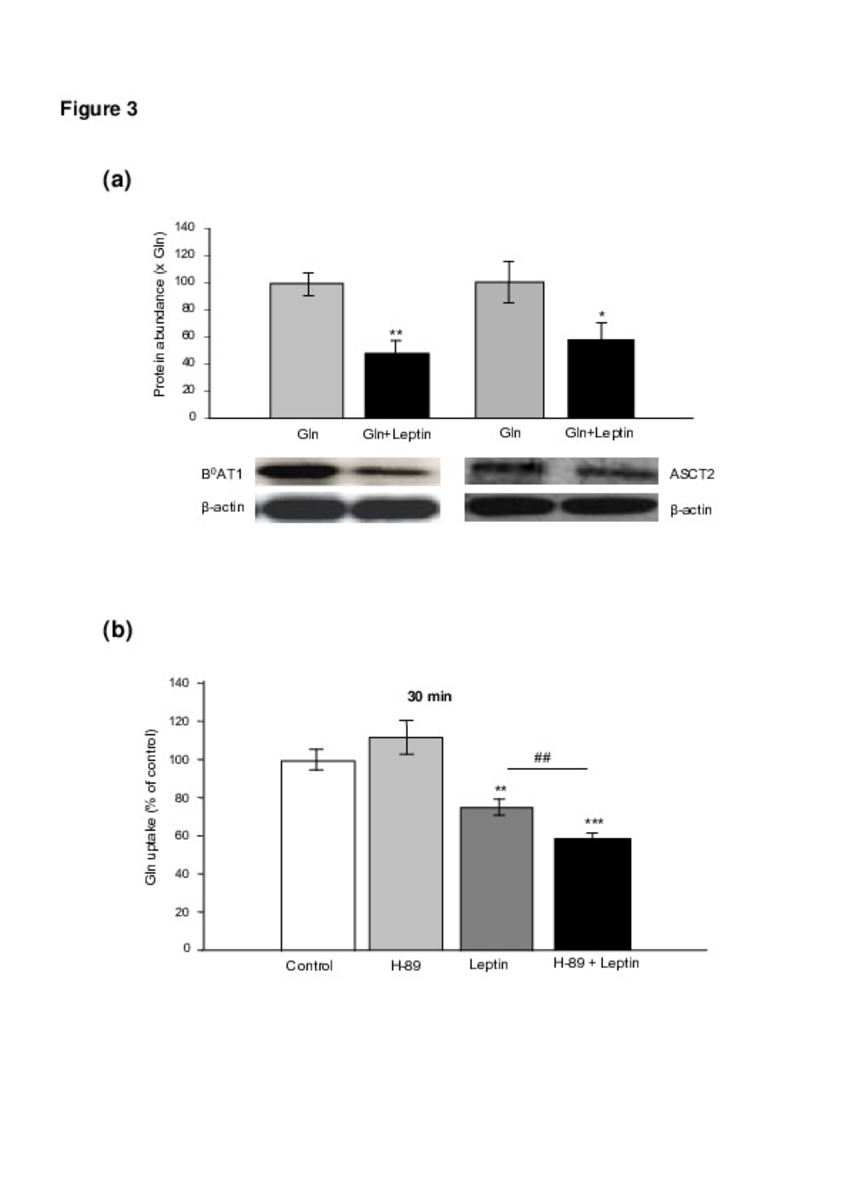
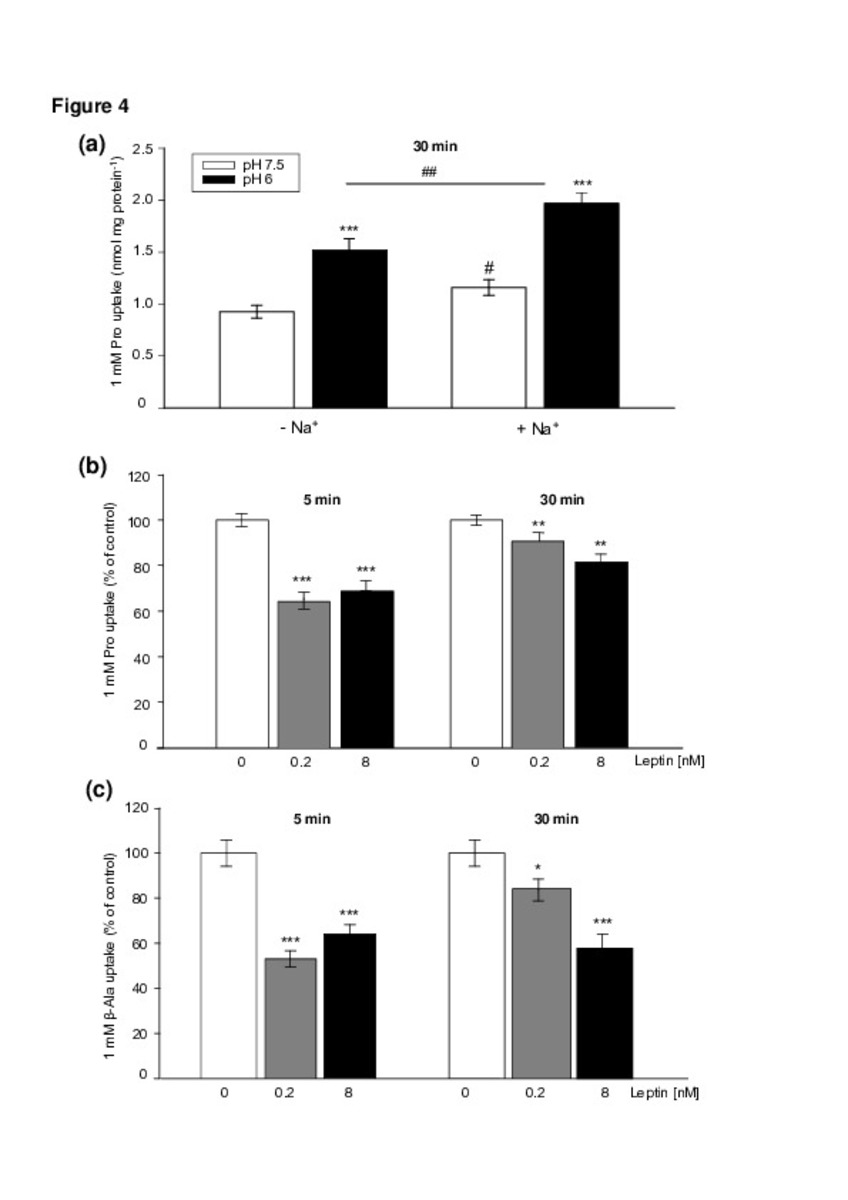
Leptin regulates sugar and amino acids transport in the human intestinal cell line Caco-2
Palabras clave :
Amino acid transporters
Caco-2 cells
Leptin
Sodium-dependent glucose transporter 1
Western blot
Fecha de publicación :
2012
Cita:
Fanjul C, Barrenetxe J, Inigo C, Sakar Y, Ducroc R, Barber A, et al. Leptin regulates sugar and amino acids transport in the human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2012 May;205(1):82-91
Aparece en las colecciones:
Estadísticas e impacto
0 citas en

0 citas en

Los ítems de Dadun están protegidos por copyright, con todos los derechos reservados, a menos que se indique lo contrario.