Full metadata record
| DC Field | Value | Language |
|---|---|---|
| dc.creator | Becares, N. (Natalia) | - |
| dc.creator | Gage, M.C. (Matthew C.) | - |
| dc.creator | Voisin, M. (Maud) | - |
| dc.creator | Shrestha, E. (Elina) | - |
| dc.creator | Martin-Gutierrez, L. (Lucina) | - |
| dc.creator | Liang, N. (Ning) | - |
| dc.creator | Louie, R. (Rikah) | - |
| dc.creator | Pourcet, B. (Benoit) | - |
| dc.creator | Pello, O.M. (Oscar M.) | - |
| dc.creator | Luong, T.V. (Tu Vinh) | - |
| dc.creator | Goñi, S. (Saioa) | - |
| dc.creator | Pichardo-Almarza, C. (Cesar) | - |
| dc.creator | Roberg-Larsen, H. (Hanne) | - |
| dc.creator | Diaz-Zuccarini, V. (Vanessa) | - |
| dc.creator | Steffensen, K.R. (Knut R. ) | - |
| dc.creator | O’Brien, A. (Alastair) | - |
| dc.creator | Garabedian, M.J. (Michael J.) | - |
| dc.creator | Rombouts, K. (Krista) | - |
| dc.creator | Treuter, E. (Eckardt) | - |
| dc.creator | Pineda-Torra, I. (Inés) | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2022-03-11T13:50:37Z | - |
| dc.date.available | 2022-03-11T13:50:37Z | - |
| dc.date.issued | 2019 | - |
| dc.identifier.citation | Becares, N. (Natalia); Gage, M.C. (Matthew C.); Voisin, M. (Maud); et al. "Impaired LXRa phosphorylation attenuates progression of fatty liver disease". Elsevier BV. 26 (4), 2019, 984 - 995 | es |
| dc.identifier.issn | 2211-1247 | - |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/10171/63165 | - |
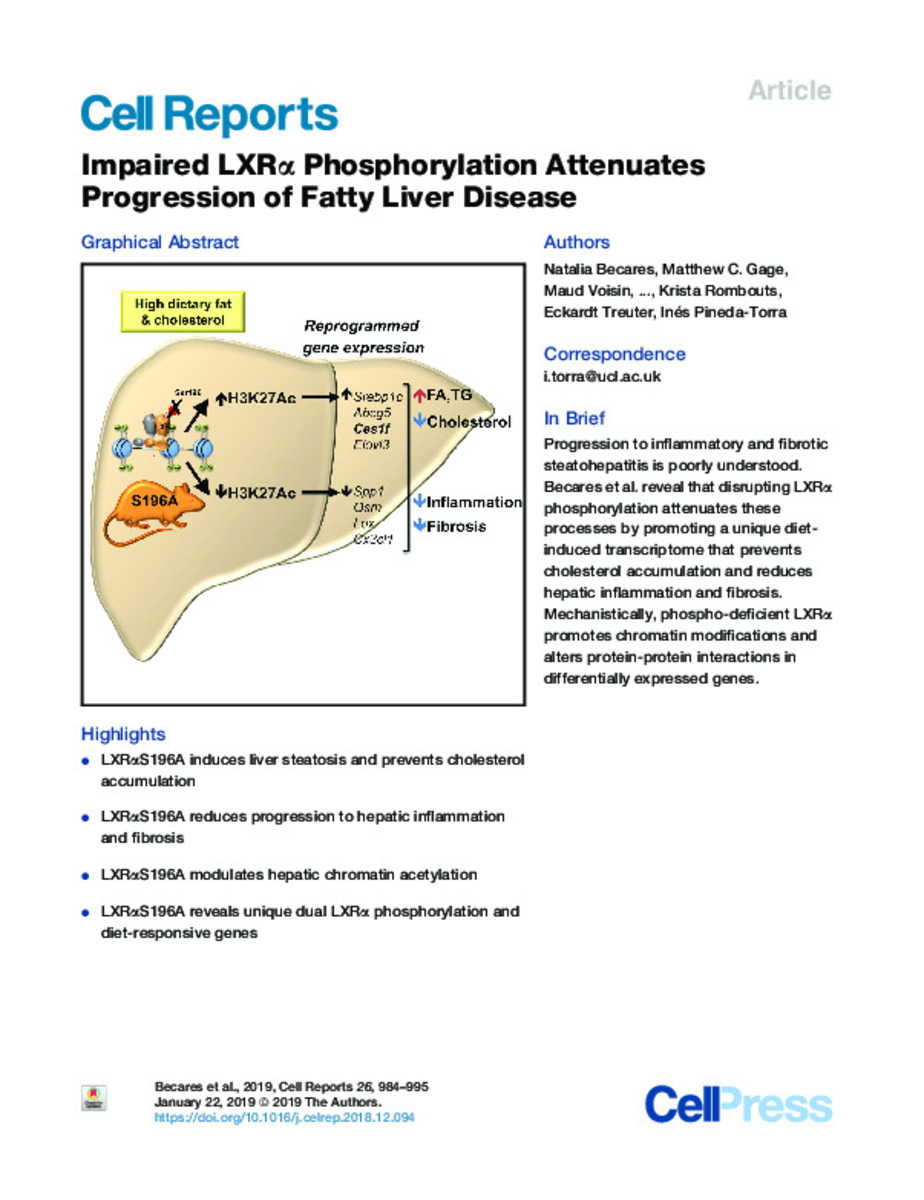
| dc.description.abstract | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a very common indication for liver transplantation. How fat-rich diets promote progression from fatty liver to more damaging inflammatory and fibrotic stages is poorly understood. Here, we show that disrupting phosphorylation at Ser196 (S196A) in the liver X receptor alpha (LXRα, NR1H3) retards NAFLD progression in mice on a high-fat-high-cholesterol diet. Mechanistically, this is explained by key histone acetylation (H3K27) and transcriptional changes in pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory genes. Furthermore, S196A-LXRα expression reveals the regulation of novel diet-specific LXRα-responsive genes, including the induction of Ces1f, implicated in the breakdown of hepatic lipids. This involves induced H3K27 acetylation and altered LXR and TBLR1 cofactor occupancy at the Ces1f gene in S196A fatty livers. Overall, impaired Ser196-LXRα phosphorylation acts as a novel nutritional molecular sensor that profoundly alters the hepatic H3K27 acetylome and transcriptome during NAFLD progression placing LXRα phosphorylation as an alternative anti-inflammatory or anti-fibrotic therapeutic target. | es_ES |
| dc.description.sponsorship | This work was supported by a Medical Research Council New Investigator Grant G0801278 (I.P.-T.), British Heart Foundation Project Grants PG/13/10/30000 (I.P.-T.) and PG/16/87/32492 (M.C.G.), UCL Grand Challenges PhD Studentship (N.B. and I.P.-T.), Academy of Medical Sciences Newton Advanced Fellowship (I.P.-T.), Royal Free Charity (I.P.-T.), University of Oslo DIATECH@UiO initiative (H.R.-L.), the Centre for Innovative Medicine at the Karolinska Institute grant CIMED-2-391/2016 (E.T.), the Swedish Research Council grant VR-2016- 01743 (E.T.), the Swedish Cancer Society grant CAN-2015/609 (E.T.), the Swedish Diabetes Foundation grant DIA2016-157 (E.T.), the Novo Nordisk Foundation grant NN2017-21086 (E.T.), and the European Union FP7 HEALTH program grant HUMAN-F5-2013-602757 (E.T.). M.J.G. and M.V. were supported by NIH R01HL117226. C.P.-A. and V.D.-Z. received support by the EPSRC grant (EP/L000296/1) and the Leverhulme Trust Senior Research Fellowship (RF-2015-482) and V.D.-Z. by the Wellcome/EPSRC Centre for Interventional and Surgical Sciences grant (203145Z/16/Z). | es_ES |
| dc.language.iso | eng | es_ES |
| dc.publisher | Elsevier BV | es_ES |
| dc.relation | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/EC/FP7/602757/EU | - |
| dc.relation | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/NIH/NATIONAL_HEART,_LUNG,_AND_BLOOD_INSTITUTE/5R01HL117226-03/US | - |
| dc.relation | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/EPSRC/UKRI/EP%2FL000296%2F1/GB/Personalised Medicine through Learning in the Model Space// | - |
| dc.relation | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/MRC/UKRI/G0801278/GB/Role of LXR alpha phosphorylation in macrophage activation and atherogenesis// | - |
| dc.rights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Liver X receptor | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Phosphorylation | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Liver | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Lipid metabolism | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Inflammation | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Fibrosis | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Transcription | es_ES |
| dc.subject | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | es_ES |
| dc.title | Impaired LXRa phosphorylation attenuates progression of fatty liver disease | es_ES |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article | es_ES |
| dc.description.note | This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). | es_ES |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.094 | - |
| dadun.citation.endingPage | 995 | es_ES |
| dadun.citation.number | 4 | es_ES |
| dadun.citation.publicationName | Elsevier BV | es_ES |
| dadun.citation.startingPage | 984 | es_ES |
| dadun.citation.volume | 26 | es_ES |
Files in This Item:
Statistics and impact
Items in Dadun are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.